Bypassing reCAPTCHAs With Open Source and Commercial Tools - Part 2
Testing tools for bypassing ReCAPTCHA V3
In part 1, Pierluigi explored ReCAPTCHA’s history, the evolution from v1 to v3, and tested open-source and commercial tools to bypass v3 (the latest and most challenging reCAPTCHA version). Next, I’ll build on that article to explore how other solutions can be applied to bypass ReCAPTCHA v3!
Before proceeding, let me thank Decodo, the platinum partner of the month. They are currently running a 50% off promo on our residential proxies using the code RESI50.
What I’m Going to Do Here
In this article, I’ll continue Pierluigi’s research to test additional solutions (both free and commercial) to see which ones can successfully bypass reCAPTCHA v3 on the selected target site.
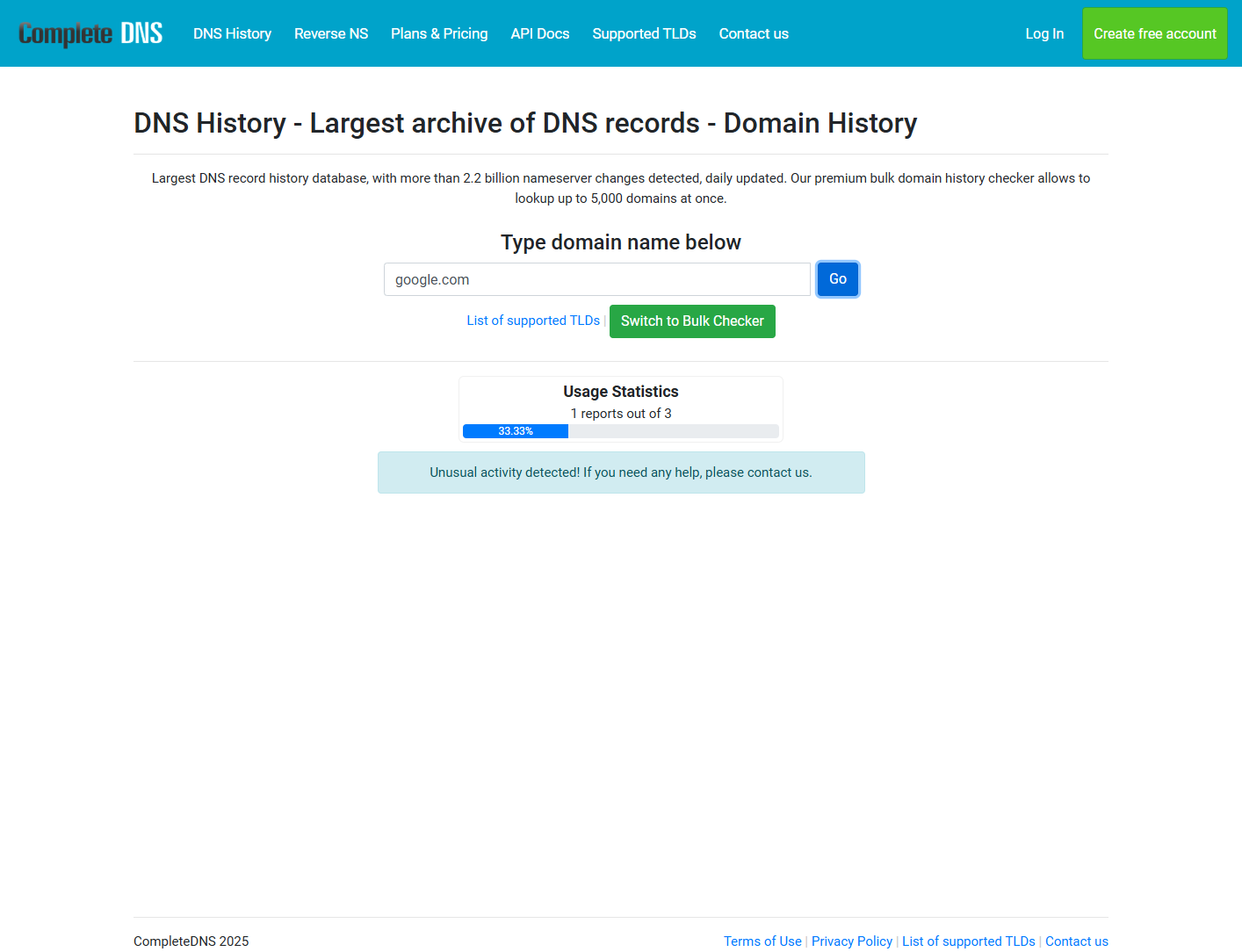
To confirm that the bypass works, submitting the form should result in a response like this:
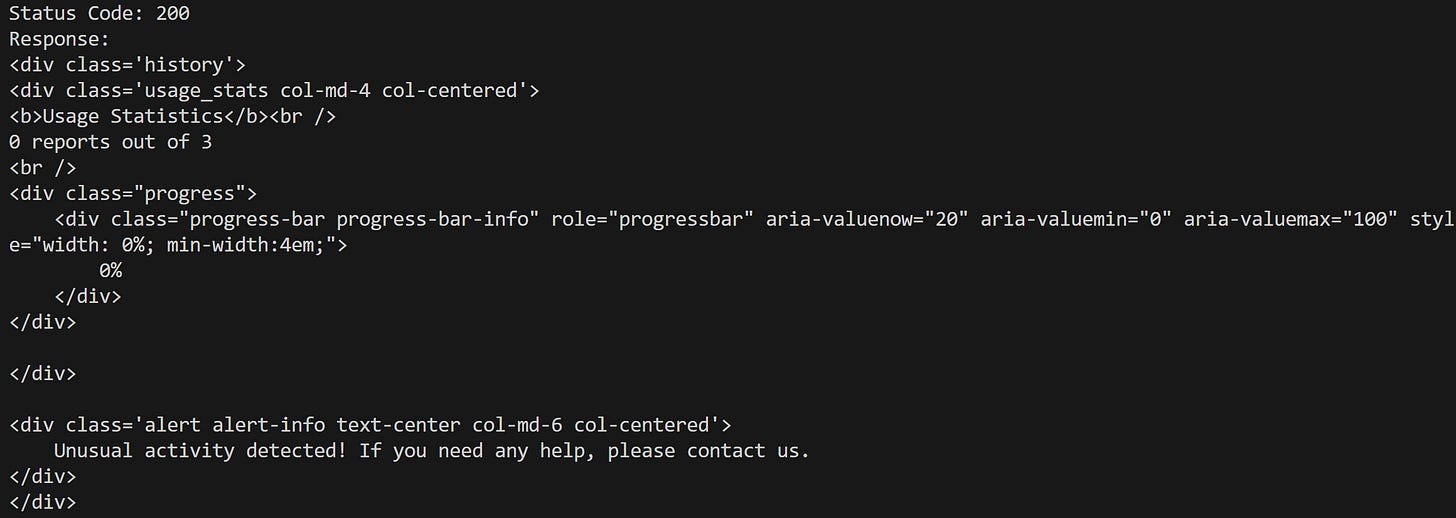
Any attempt that instead results in this HTML should be considered a failure:
Note: The code snippets shown in this blog post aren’t necessarily production-ready. The goal is to quickly test whether each solution can bypass reCAPTCHA v3. As such, the examples may include hard waits, hardcoded API keys, and other code smells.
Let me now introduce and test six other tools for bypassing ReCAPTCHA v3!
This episode is brought to you by our Gold Partners. Be sure to have a look at the Club Deals page to discover their generous offers available for the TWSC readers.
🧞 - Reliable APIs for the hard to knock Web Data Extraction: Start the trial here
💰 - Use the coupon WSC50 for a 50% off on mobile proxies and proxy builder software
NextCaptcha ❌
NextCaptcha is somewhat of an esoteric CAPTCHA solver. There isn’t much official documentation on how to use it, so you have to get a bit creative to make it work.
Based on my personal experience with the tool, I was able to get it working for reCAPTCHA v3 bypass by following the procedure I’m about to describe (I’m not sure if that's the best or only way to do it, though).
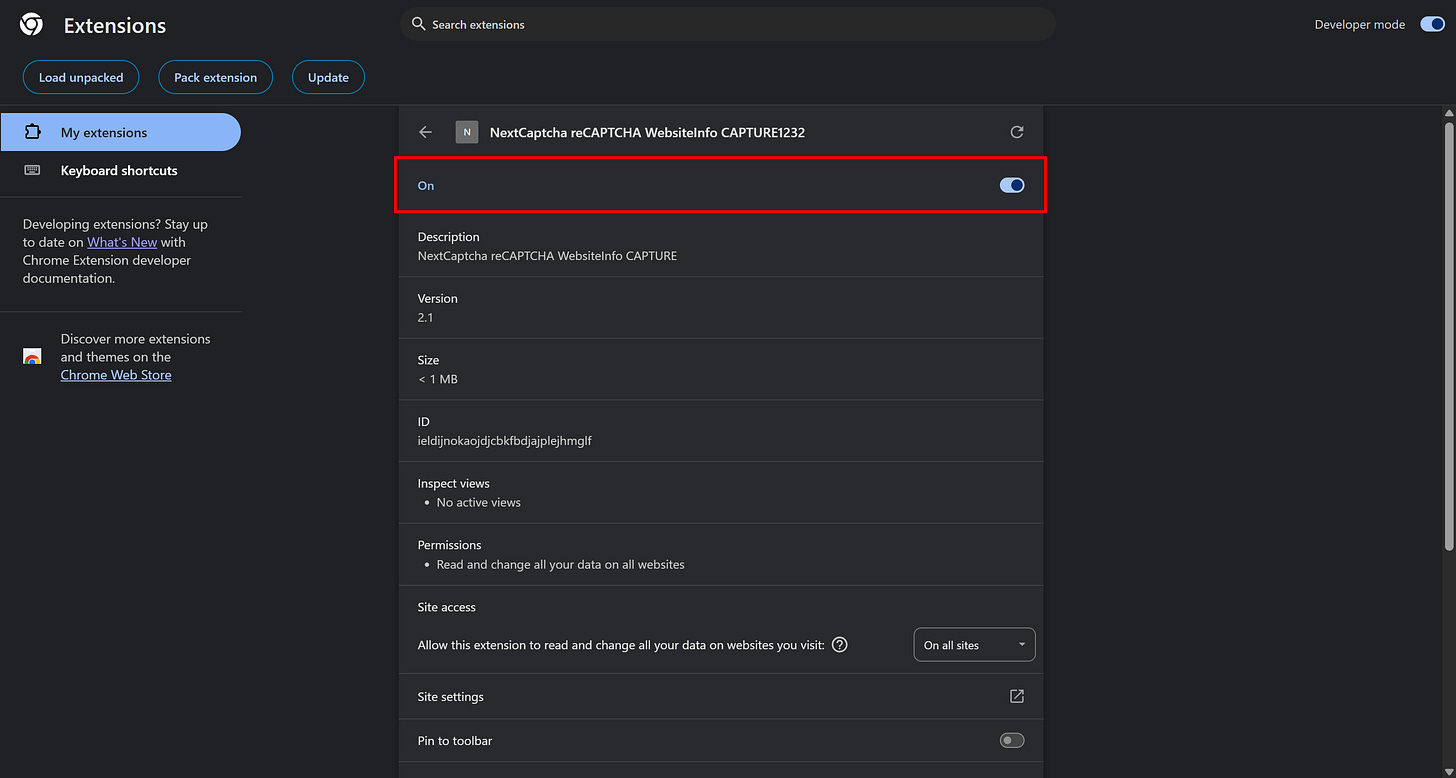
Start by creating a NextCaptcha account, buying some credits, and retrieving your API key. Then, install the NextCaptcha reCAPTCHA WebsiteInfo CAPTURE extension as explained in the official guide. Make sure it is enabled in your browser (Chrome, in my case):
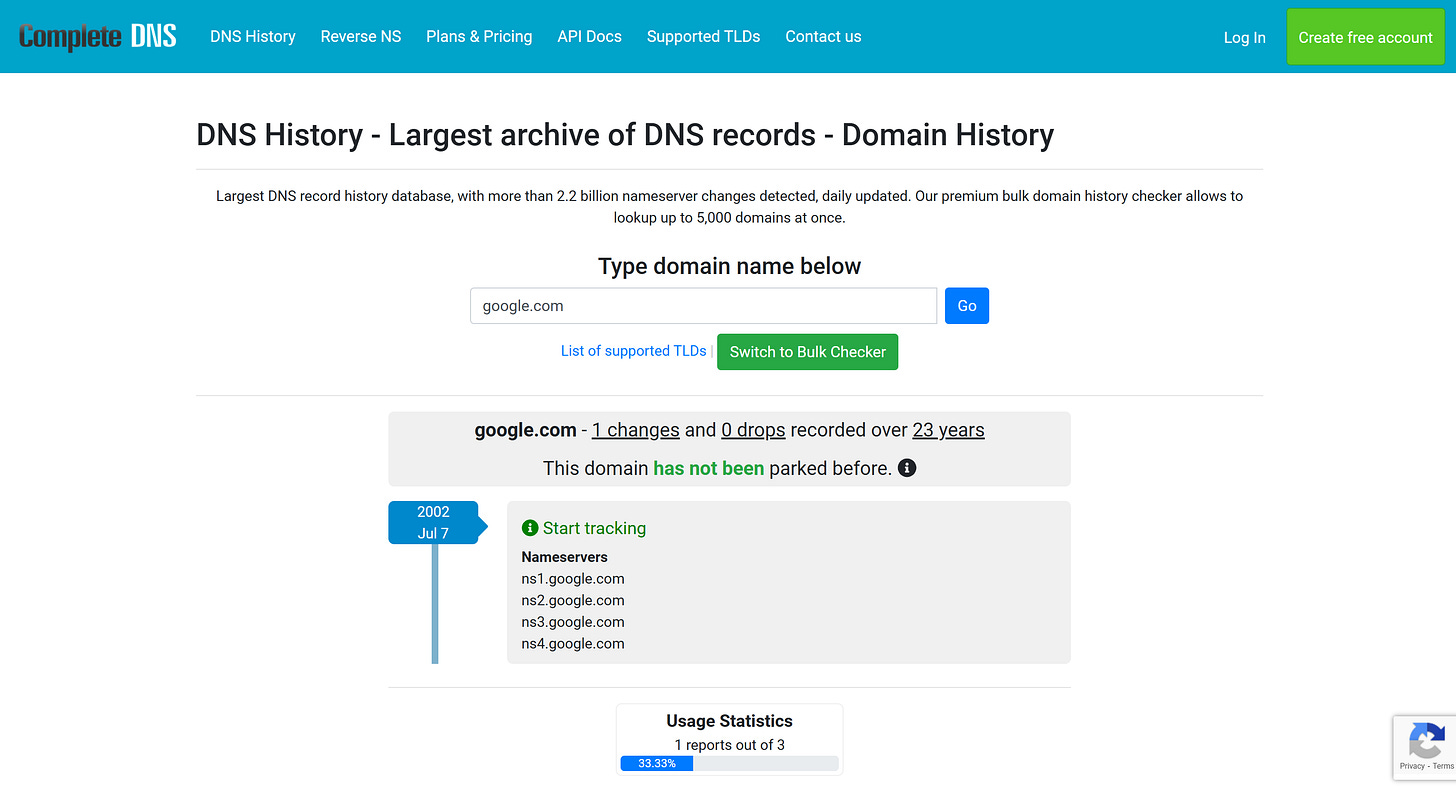
Restart your browser. Now, go to the target page in your browser, open the developer console, and perform the required interaction involving reCAPTCHA v3 verification (in this case, filling out the form and pressing “Go”).
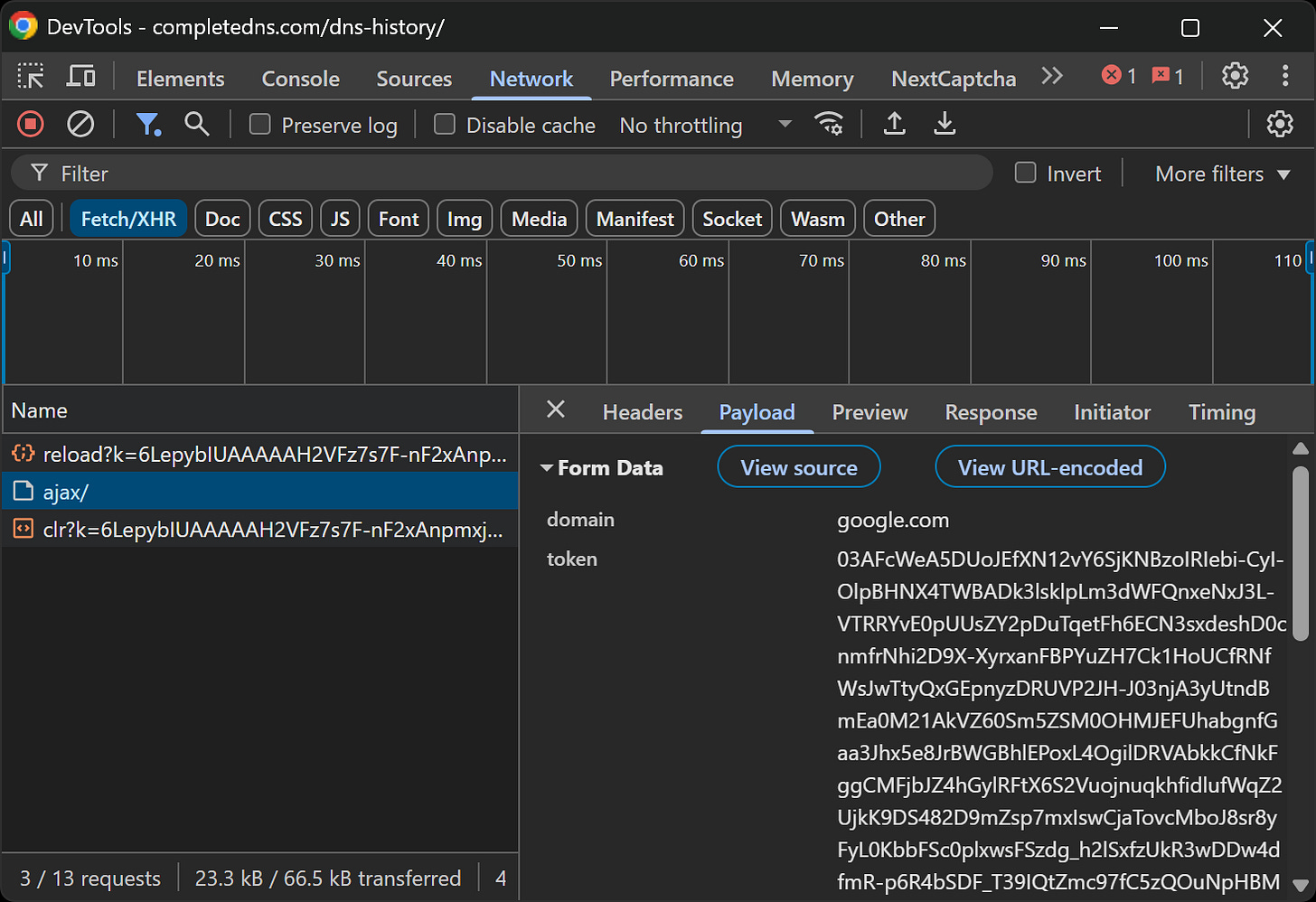
In the “Network” section, you’ll see that the page makes an AJAX request to the https://completedns.com/dns-history/ajax/ endpoint, using a payload like this:
In the payload, the token field represents the reCAPTCHA v3 resolution token returned by the Google reCAPTCHA verification endpoint (which you can also see in the “Network” tab, right before the ajax/ call).
Important: Make sure the Nextcaptcha: CAPTCHA Solver (if installed in your browser) is disabled during this step. In my experience, the NextCaptcha reCAPTCHA WebsiteInfo CAPTURE extension conflicts with the main Nextcaptcha: CAPTCHA Solver, and neither works properly if both are enabled at the same time.
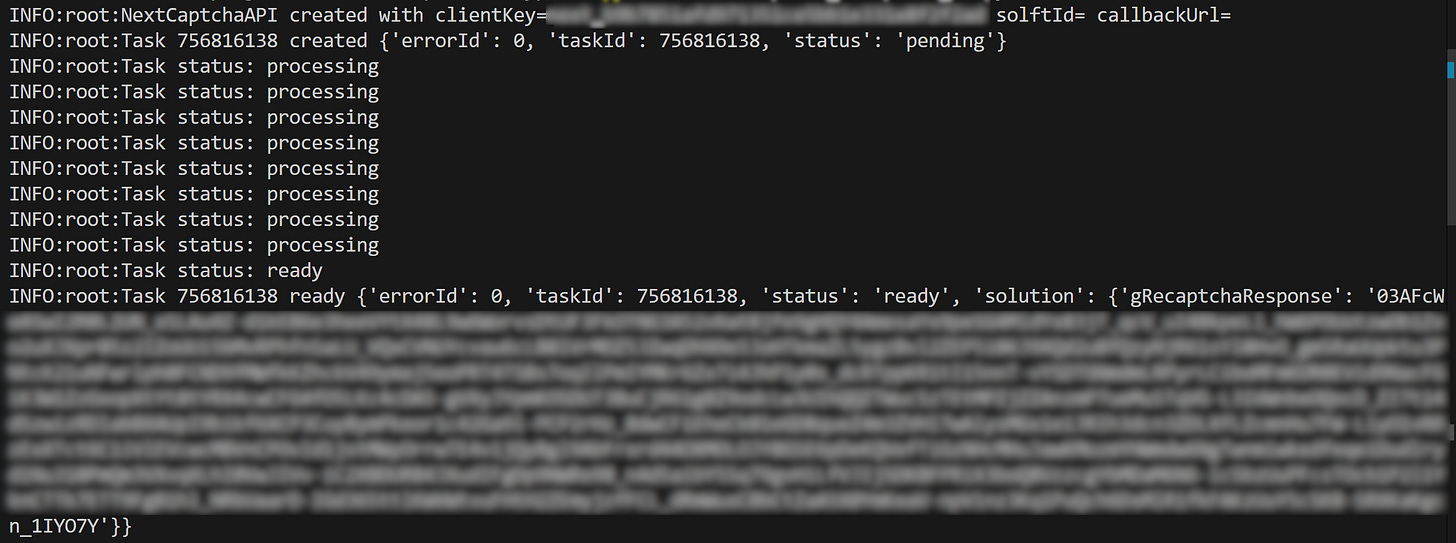
At this point, open the “NextCaptcha” tab in your DevTools. You should see a JSON string similar to this:
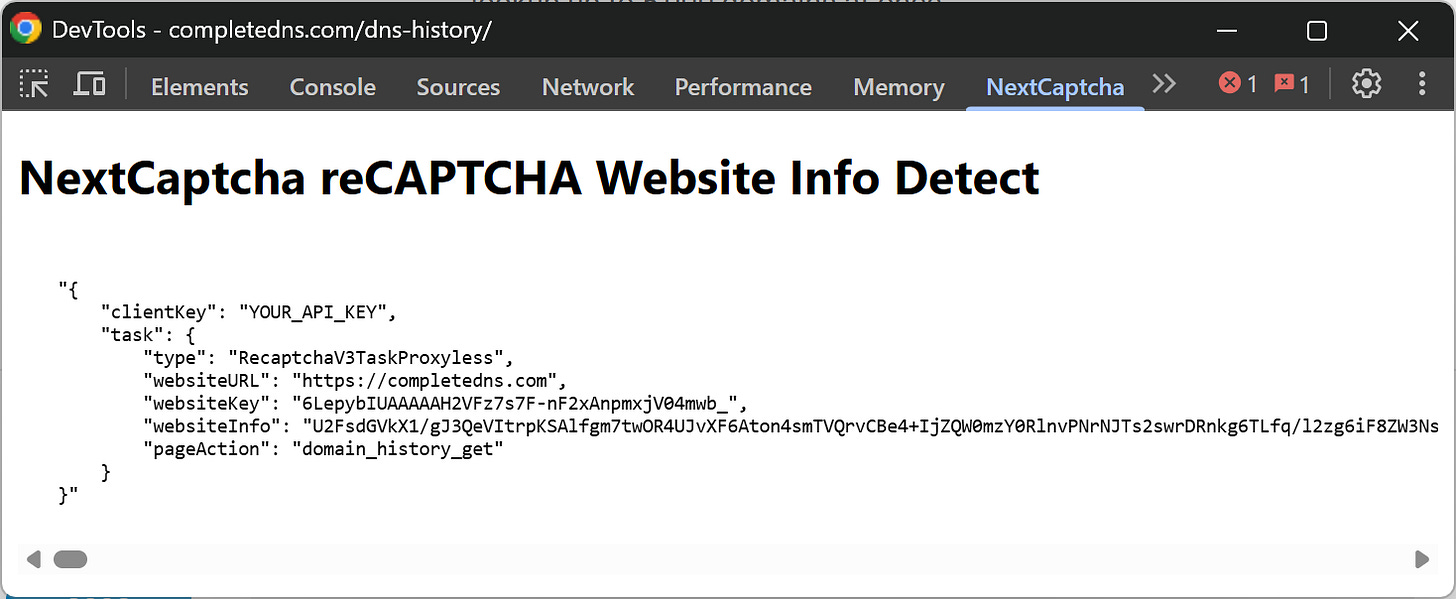
The JSON strings above contain the site's reCAPTCHA key (the websiteKey field), the target URL, the reCAPTCHA page action, and other relevant information.
Specifically, that JSON string is the payload you need to send to the NextCaptcha APIs (after replacing clientKey with your actual NextCaptcha API key, of course) in order to programmatically replicate the reCAPTCHA v3-protected action (which is the call to the https://completedns.com/dns-history/ajax/ endpoint seen earlier).
To achieve the reCAPTCHA v3 bypass goal, you can either manually call the NextCaptcha API directly, like this:
# pip install requests
import requests
import time
# Your NextCaptcha API key (replace with your actual key)
next_captcha_api_key = "XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX"
# Info extracted from the JSON provided by the NextCaptcha reCAPTCHA WebsiteInfo CAPTURE extension
website_url = "https://completedns.com"
website_key = "6LepybIUAAAAAH2VFz7s7F-nF2xAnpmxjV04mwb_"
page_action = "domain_history_get"
website_info = "U2F..." # Replace with the actual string captured by the extension
# Step 1: Create a reCAPTCHA solving task
create_task_url = "https://api.nextcaptcha.com/createTask"
headers = {
"Content-Type": "application/json",
"Accept": "application/json",
}
payload = {
"clientKey": next_captcha_api_key,
"task": {
"type": "RecaptchaV3TaskProxyless",
"websiteURL": website_url,
"websiteKey": website_key,
"websiteInfo": website_info,
"pageAction": page_action
}
}
print("Submitting task to NextCaptcha...")
response = session.post(create_task_url, headers=headers, json=payload)
data = response.json()
print(response.text)
# Initializer where to store the reCAPTCHA solution token
token = None
# Step 2: Poll for the task result
if data.get("status") == "ready":
token = data.get("solution", {}).get("gRecaptchaResponse")
elif data.get("status") == "pending":
# Polling logic...
task_id = data.get("taskId")
get_result_url = "https://api.nextcaptcha.com/getTaskResult"
poll_payload = {
"clientKey": next_captcha_api_key,
"taskId": task_id
}
print("Polling for CAPTCHA solution...")
while True:
time.sleep(3)
poll_response = session.post(get_result_url, headers=headers, json=poll_payload)
print(poll_response.text)
try:
poll_response.raise_for_status()
poll_data = poll_response.json()
if poll_data.get("status") == "ready":
token = poll_data.get("solution", {}).get("gRecaptchaResponse")
break
elif poll_data.get("status") == "failed":
print("CAPTCHA solving failed.")
break
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error while polling: {e}")
break
else:
print("Failed to create the task.")
# Step 3: Use the reCAPTCHA token to replicate the protected action
ajax_url = "https://completedns.com/dns-history/ajax/"
headers = {
"accept": "*/*",
"accept-language": "en-US,en;q=0.8",
"cache-control": "no-cache",
"content-type": "application/x-www-form-urlencoded; charset=UTF-8",
"dnt": "1",
"origin": "https://completedns.com",
"pragma": "no-cache",
"priority": "u=1, i",
"referer": "https://completedns.com/dns-history/",
"sec-ch-ua": '"Not)A;Brand";v="8", "Chromium";v="138", "Brave";v="138"',
"sec-ch-ua-mobile": "?0",
"sec-ch-ua-platform": '"macOS"',
"sec-fetch-dest": "empty",
"sec-fetch-mode": "cors",
"sec-fetch-site": "same-origin",
"sec-gpc": "1",
"user-agent": "Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_15_7) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/138.0.0.0 Safari/537.36",
"x-requested-with": "XMLHttpRequest"
}
# Fill out the request payload with the reCAPTCHA token
data = {
"domain": "google.com",
"token": token
}
# Send the POST request
print("Sending request to reCAPTCHA-protected endpoint...")
response = session.post(ajax_url, headers=headers, data=data)
# Output the response
print(f"Status Code: {response.status_code}")
print(f"Response: {response.text}")Or use the NextCaptcha Python SDK as follows:
# pip install nextcaptcha-python requests
from nextcaptcha import NextCaptchaAPI
import requests
next_captcha_api_key = "next_XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX" # Replace with your NextCaptcha API key
# Initialize the NextCaptcha API client
api = NextCaptchaAPI(client_key=next_captcha_api_key)
# Info extracted from the JSON provided by the NextCaptcha reCAPTCHA WebsiteInfo CAPTURE extension
website_url = "https://completedns.com"
website_key = "6LepybIUAAAAAH2VFz7s7F-nF2xAnpmxjV04mwb_"
page_action = "domain_history_get"
# Call the reCAPTCHA v3 solving API
result = api.recaptchav3(
website_url=website_url,
website_key=website_key,
page_action=page_action
)
# Extract the reCAPTCHA token from the response
token = result["solution"]["gRecaptchaResponse"]
url = "https://completedns.com/dns-history/ajax/"
# Replicate the reCAPTCHA protected action
headers = {
"accept": "*/*",
"accept-language": "en-US,en;q=0.8",
"cache-control": "no-cache",
"content-type": "application/x-www-form-urlencoded; charset=UTF-8",
"dnt": "1",
"origin": "https://completedns.com",
"pragma": "no-cache",
"priority": "u=1, i",
"referer": "https://completedns.com/dns-history/",
"sec-ch-ua": '"Not)A;Brand";v="8", "Chromium";v="138", "Brave";v="138"',
"sec-ch-ua-mobile": "?0",
"sec-ch-ua-platform": '"macOS"',
"sec-fetch-dest": "empty",
"sec-fetch-mode": "cors",
"sec-fetch-site": "same-origin",
"sec-gpc": "1",
"user-agent": "Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_15_7) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/138.0.0.0 Safari/537.36",
"x-requested-with": "XMLHttpRequest"
}
# Fill out the request payload with the reCAPTCHA token
data = {
"domain": "google.com",
"token": token
}
response = requests.post(url, headers=headers, data=data)
# Print the response from the target server
print(f"Status Code: {response.status_code}")
print(f"Response: {response.text}")If you run the above script, you should get something like:
As you can see, the NextCaptcha SDK creates a reCAPTCHA solution task, then continuously polls until the result is ready. The resulting JSON data will have the following format:
{
"errorId": 0,
"taskId": 756816138,
"status": "ready",
"solution": {
"gRecaptchaResponse": "03AF..."
}
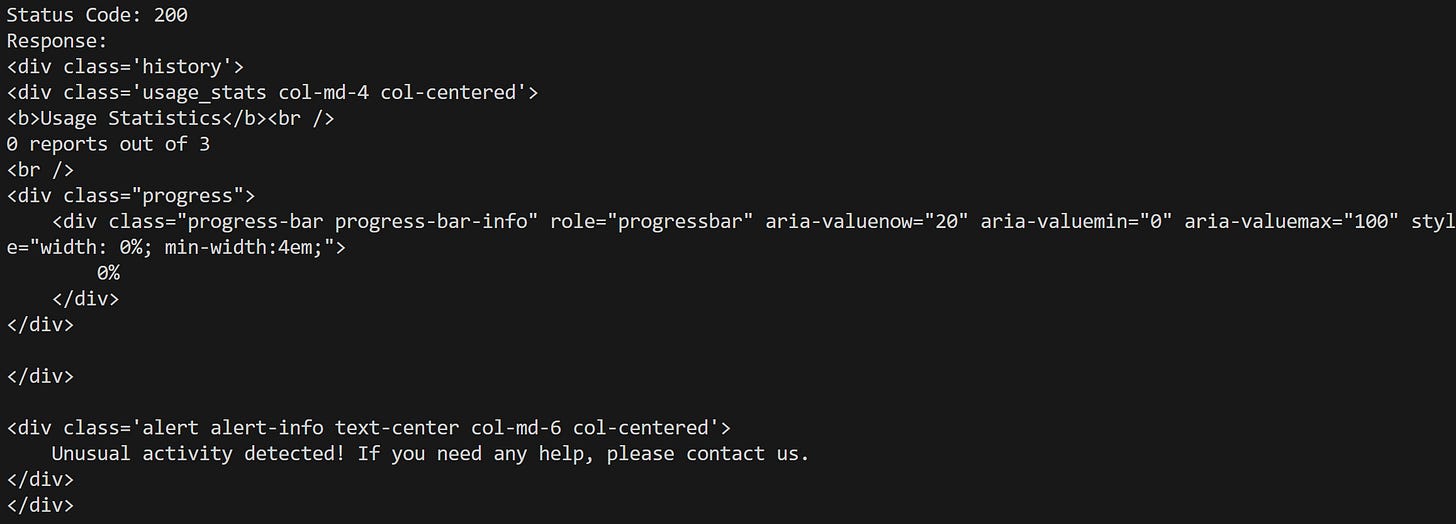
}The gRecaptchaResponse field contains the reCAPTCHA resolution token you’re interested in. When used to replicate the call to the https://completedns.com/dns-history/ajax/ endpoint, I did receive a 200 HTTP response, but the response body contained an error HTML response instead of the expected result:
This might be because the CAPTCHA validation failed or the target site applied additional anti-bot checks. (Both Pierluigi and I also tried with hrequests and curl_cffi for TLS fingerprint spoofing, but that didn’t work either.)
Now, while I wasn’t successful with it myself on the chosen target page, Pierluigi has personally integrated NextCaptcha to bypass reCAPTCHA v3 on a real-world project. So much depends on the site you are working on, and having multiple reCAPTCHA bypass options to test definitely helps (which is why, after consulting with Pierluigi, I decided to mention NextCaptcha here).
Before continuing with the article, I wanted to let you know that I've started my community in Circle. It’s a place where we can share our experiences and knowledge, and it’s included in your subscription. Enter the TWSC community at this link.
CapSolver ✅
CapSolver is an AI-powered captcha solver that can handle reCAPTCHA, Cloudflare challenges, and other types of captchas. It supports both API integration and an open-source browser extension.
To get started, sign up for CapSolver, deposit some funds, and get your API key. Now, install the CapSolver Python SDK and use it to simulate the reCAPTCHA-protected action on your target page:
# pip install capsolver requests
import os
# Set the CapSolver API key in the envs
os.environ["CAPSOLVER_API_KEY"]="XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX" # Replace with your CapSolver API key
import capsolver
import requests
# Call the reCAPTCHA v3 solving service
url = "https://completedns.com/dns-history"
website_key = "6LepybIUAAAAAH2VFz7s7F-nF2xAnpmxjV04mwb_"
solution = capsolver.solve({
"type": "ReCaptchaV3TaskProxyLess",
"websiteURL": url,
"websiteKey": website_key,
})
print(solution)
# Extract the User-Agent and token from the response
token = solution["gRecaptchaResponse"]
user_agent = solution["userAgent"]
# Replicate the reCAPTCHA-protected API call
url = "https://completedns.com/dns-history/ajax/"
headers = {
"accept": "*/*",
"accept-language": "en-US,en;q=0.8",
"cache-control": "no-cache",
"content-type": "application/x-www-form-urlencoded; charset=UTF-8",
"dnt": "1",
"origin": "https://completedns.com",
"pragma": "no-cache",
"priority": "u=1, i",
"referer": "https://completedns.com/dns-history/",
"sec-ch-ua": '"Not)A;Brand";v="8", "Chromium";v="138", "Brave";v="138"',
"sec-ch-ua-mobile": "?0",
"sec-ch-ua-platform": '"macOS"',
"sec-fetch-dest": "empty",
"sec-fetch-mode": "cors",
"sec-fetch-site": "same-origin",
"sec-gpc": "1",
"user-agent": user_agent,
"x-requested-with": "XMLHttpRequest"
}
# Populate the request payload with the reCAPTCHA token
data = {
"domain": "google.com",
"token": token
}
response = requests.post(url, headers=headers, data=data)
# Print the response from the target server
print(f"Status Code: {response.status_code}")
print(f"Response:{response.text}")Note: The os.environ["CAPSOLVER_API_KEY"] line must be placed before importing the capsolver module. This is because the capsolver library attempts to read the CAPSOLVER_API_KEY environment variable immediately upon import. So, it must already be set.
This time, the solution variable will contain this data:
{
"createTime": 1753105226837,
"gRecaptchaResponse": "03AF...",
"userAgent": "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/137.0.0.0 Safari/537.36"
}
Note that, in addition to the reCAPTCHA v3 solution token (gRecaptchaResponse), the response also includes the User-Agent header string that was used to bypass reCAPTCHA. Using this exact User-Agent in your subsequent requests may help reduce the risk of blocks or detection.
Tip: If you’re wondering how to get the reCAPTCHA site key, one of the easiest ways is to inspect the “Network” tab in your browser's DevTools and look for Google reCAPTCHA requests:
Now, if you run the Python script mentioned above, you’ll get a 200 OK HTTP response. Still, again, the payload will contain error HTML instead of the expected data:
Luckily, there's another option!
Since CapSolver also offers a browser extension, I decided to install it and configure it in my browser to see if it could solve the reCAPTCHA v3 challenge directly on the page. To my surprise, it worked! (This proves the issue with the API call likely isn't due to the token itself, but something else in the request flow.)
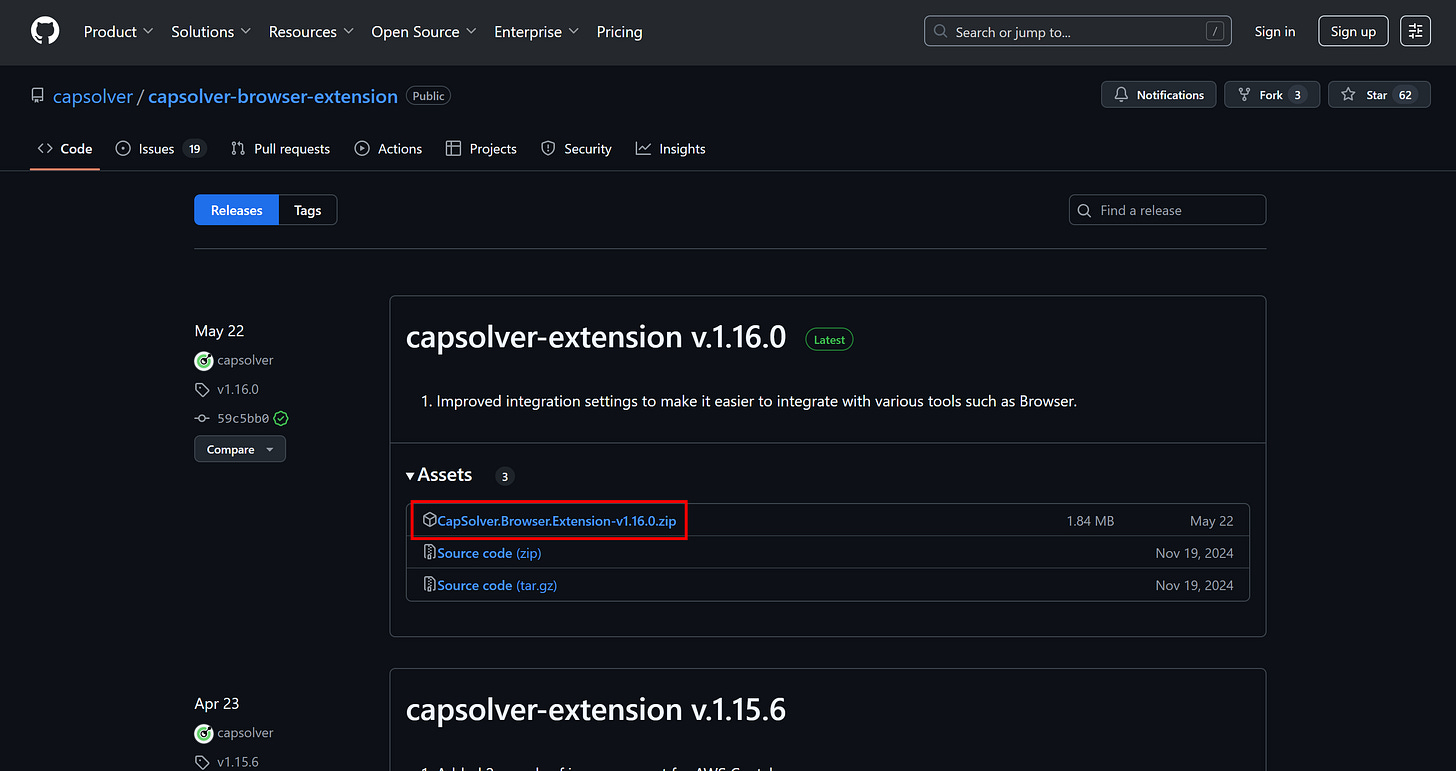
Thanks to the open-source nature of the CapSolver extension, I figured I could download it and programmatically integrate it into a Playwright script that mimics the necessary user interaction to submit the form on the target page.
So, I downloaded the extension from GitHub:
Then, I unzipped it and placed it in an extensions/ subfolder inside my Playwright project:
playwright-project
├───extensions
│ └───CapSolver.Browser.Extension-v1.16.0 # CapSolver extension
│ └─── ...
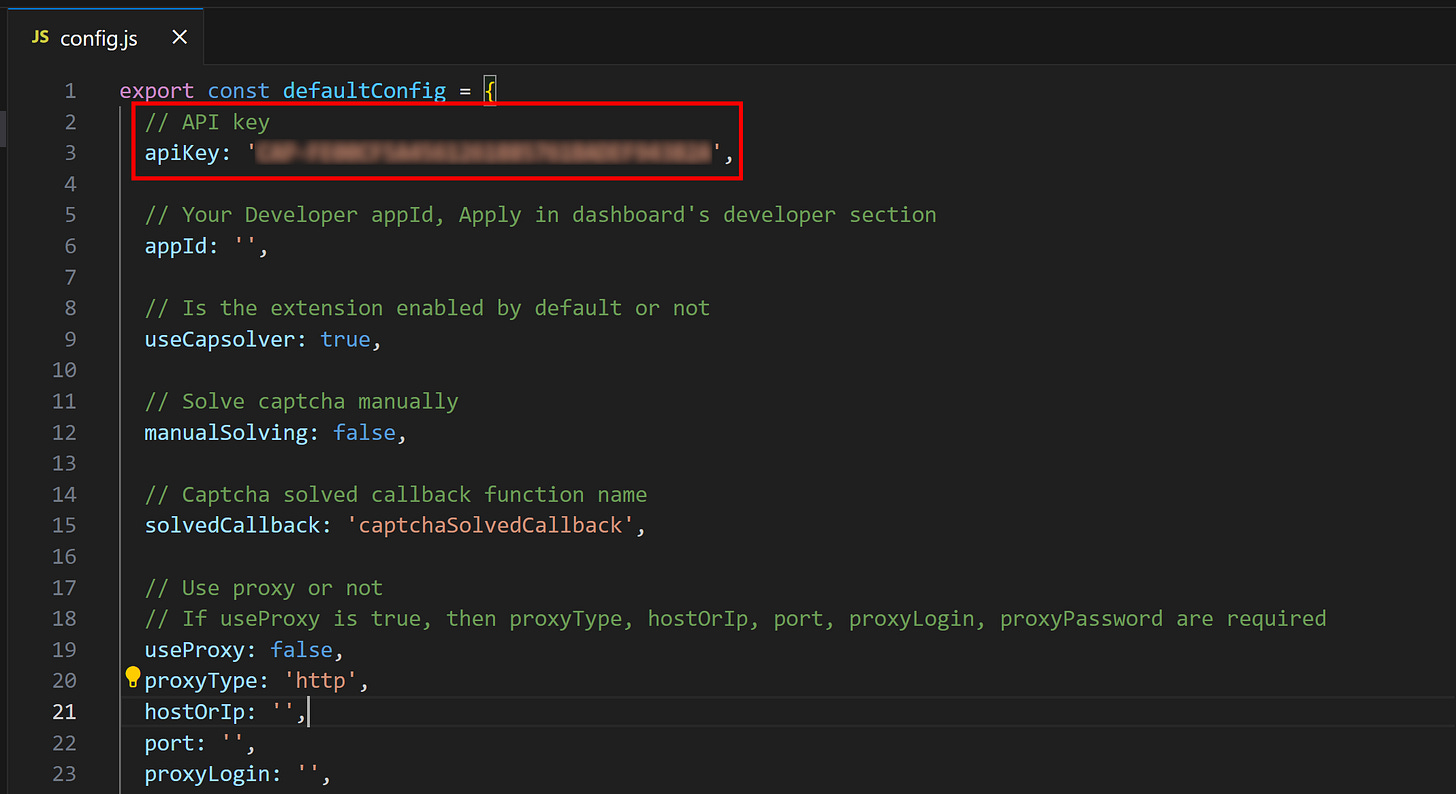
└───script.py I then opened the config.js file and replaced the apiKey variable with my CapSolver API key, saving the changes before proceeding:
This integration is better explained in the official guide for integrating CapSolver in Playwright.
After that, I imported and loaded the extension in my Playwright script while replicating the form interaction with the following code:
# pip install playwright
# python -m playwright install
from playwright.sync_api import sync_playwright
from pathlib import Path
import time
# Path to the CapSolver extension
CAPSOLVER_EXTENSION_PATH = str(Path("./extensions/CapSolver.Browser.Extension-v1.16.0").resolve())
with sync_playwright() as p:
# Use Chromium with a persistent context to load the the CapSolver extension
context = p.chromium.launch_persistent_context(
user_data_dir="/tmp/playwright-capsolver-profile", # Set to a local tmp folder path
headless=False, # Must be False to load extensions
args=[
f"--disable-extensions-except={CAPSOLVER_EXTENSION_PATH}",
f"--load-extension={CAPSOLVER_EXTENSION_PATH}"
]
)
# Reach the target page
page = context.new_page()
page.goto("https://completedns.com/dns-history")
# Wait for the page to load
time.sleep(10)
# Submit the form
page.locator("input#domain").fill("google.com")
page.locator("button[type='submit']").click()
# Wait for CAPTCHA resolution and response from the server
time.sleep(10)
# Print the current viewport
page.screenshot(path="screenshot.png", full_page=True)
# Close the browser and release its resources
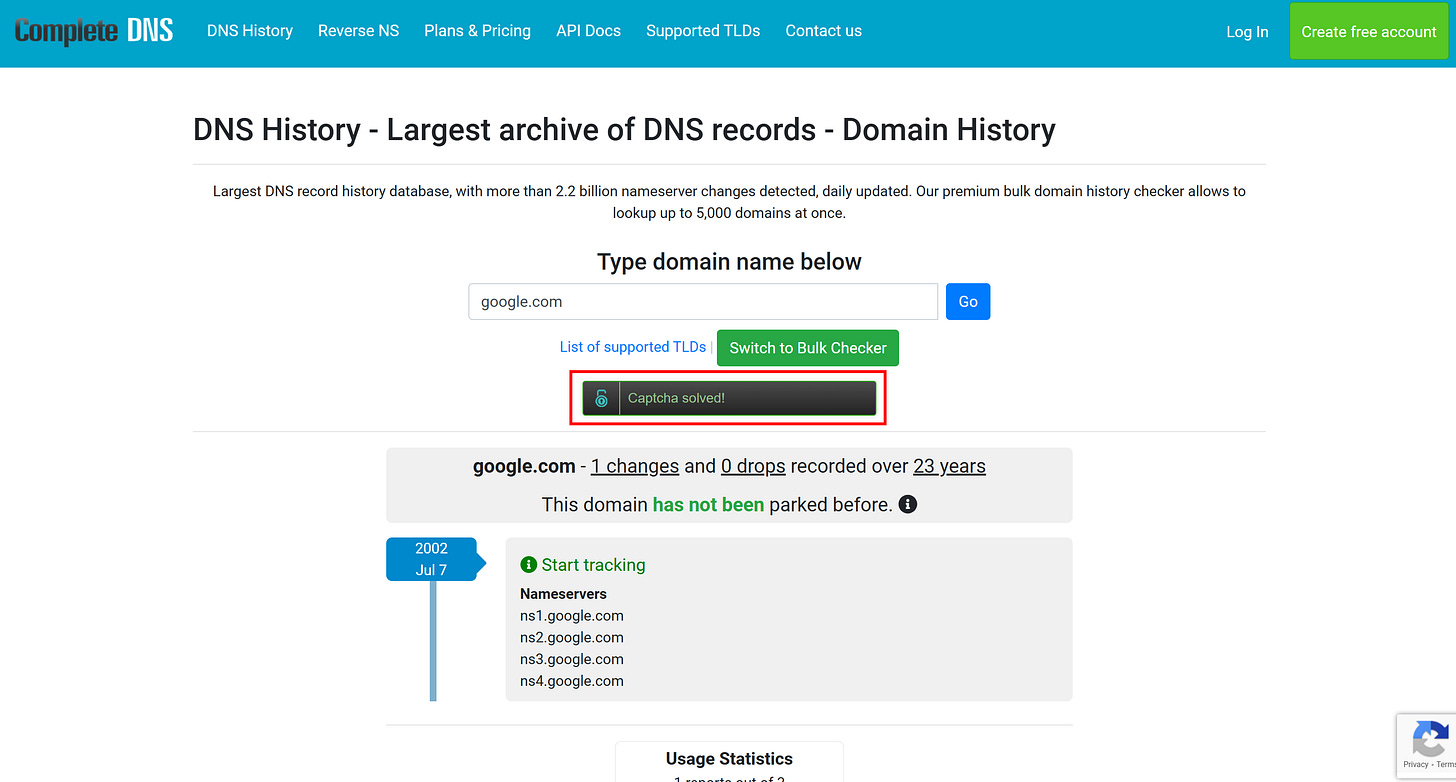
context.close()To confirm that it worked, I instructed the script to generate a screenshot in the end via the Playwright screenshot() method. The resulting screenshot.png file produced by the script should contain:
As you can tell, the form was successfully submitted. On the right (just below the reCAPTCHA info iframe), you’ll notice a small indicator showing that the reCAPTCHA was solved by CapSolver.
So, while the direct API integration didn’t work in this case, the open-source nature of the CapSolver extension allows you to integrate it programmatically into Playwright, making it a viable solution for solving reCAPTCHA v3 in browser automation.
2Captcha ❌
2Captcha is one of the most popular and widely used CAPTCHA solving services, with over 2,300 reviews on Trustpilot.
To try it out, sign up for 2Captcha and load some credits. Install the 2Captcha browser extension and register your 2Captcha API key inside it.
Now, when visiting a target site that uses reCAPTCHA, the extension will attempt to solve it for you in real time. As shown below, it should work:
2CAptcha clearly doesn’t help much in this particular case. The reason is that you're dealing with reCAPTCHA v3, which is invisible and already passes if you're a human using a real-world browser (as you should be).
That said, it proves that 2Captcha can bypass reCAPTCHA v3 successfully. The main issue is that, unlike CapSolver, the 2Captcha extension isn’t open source. So, you can’t download it or integrate it into Playwright via a .zip file like I demonstrated earlier for CapSolver.
That implies the only viable approach is to simulate the AJAX request directly, as shown in the NextCaptcha and CapSolver examples. You can do that using the 2Captcha SDK with the following code:
# pip install 2captcha-python requests
import requests
from twocaptcha import TwoCaptcha
api_key = "XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX" # Replace with your 2Captcha API key
# Initialize the 2Captcha client
solver = TwoCaptcha(api_key)
# Try to solve the reCAPTCHA v3 with 2Captcha on the target page
url = "https://completedns.com/dns-history"
website_key = "6LepybIUAAAAAH2VFz7s7F-nF2xAnpmxjV04mwb_"
result = solver.recaptcha(
sitekey=website_key,
url=url,
version="v3", # To call the reCAPTCHA v3 solving endpoint
)
# Extract the token from the response
token = result["code"]
# Replicate the reCAPTCHA-protected action
url = "https://completedns.com/dns-history/ajax/"
headers = {
"accept": "*/*",
"accept-language": "en-US,en;q=0.8",
"cache-control": "no-cache",
"content-type": "application/x-www-form-urlencoded; charset=UTF-8",
"dnt": "1",
"origin": "https://completedns.com",
"pragma": "no-cache",
"priority": "u=1, i",
"referer": "https://completedns.com/dns-history/",
"sec-ch-ua": '"Not)A;Brand";v="8", "Chromium";v="138", "Brave";v="138"',
"sec-ch-ua-mobile": "?0",
"sec-ch-ua-platform": '"macOS"',
"sec-fetch-dest": "empty",
"sec-fetch-mode": "cors",
"sec-fetch-site": "same-origin",
"sec-gpc": "1",
"user-agent": "Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_15_7) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/138.0.0.0 Safari/537.36",
"x-requested-with": "XMLHttpRequest"
}
data = {
"domain": "google.com",
"token": token
}
response = requests.post(url, headers=headers, data=data)
# Print the response data from the target server
print(f"Status Code: {response.status_code}")
print(f"Response:{response.text}")Now, the result from 2Captcha will have a structure like this:
{
"captchaId": "80167142643",
"code": "03AF..."
}As a result, you can access the reCAPTCHA validation token for bypassing reCAPTCHA v3 from the code field (and then use it to replicate the protected action).
However, as before, you’ll likely receive a 200 HTTP response with an error HTML message:
In this case as well, direct integration with the API using the retrieved reCAPTCHA v3 resolution token doesn’t work.
As mentioned earlier for NextCaptcha and CapSolver (when used via API), the 2Captcha API integration may actually work on other target sites.
SeleniumBase ✅
SeleniumBase is an open-source Python framework built on top of Selenium, optimized for advanced web automation (and testing) scenarios. One of its standout features is UC (Undetected Chrome) mode.
UC mode enables SeleniumBase bots to appear more like real users. Behind the scenes, it relies on a customized version of undetected-chromedriver. If you’re not familiar with it, undetected-chromedriver is a patched version of ChromeDriver specifically tweaked to evade detection by anti-bot services.
In simpler terms, using SeleniumBase with UC mode provides similar stealth benefits to tools like Camoufox (which Pierluigi demonstrated to work successfully against reCAPTCHA v3).
Below's how to use SeleniumBase in UC mode for bypassing reCAPTCHA v3 challenges on the target webpage:
# pip install seleniumbase
from seleniumbase import SB
import time
with SB(uc=True, headless=False) as sb:
# Open the target page in UC mode
sb.uc_open_with_reconnect("https://completedns.com/dns-history")
# Wait for the page to load
time.sleep(10)
# Fill in the domain field
sb.type("#domain", "google.com")
# Click the submit button
sb.click('button[type="submit"]')
# Wait for the results to appear
time.sleep(10)
# Take a screenshot of the entire <body> selector
sb.save_screenshot("screenshot.png", selector="body")The produced screenshot.png file should look like this:
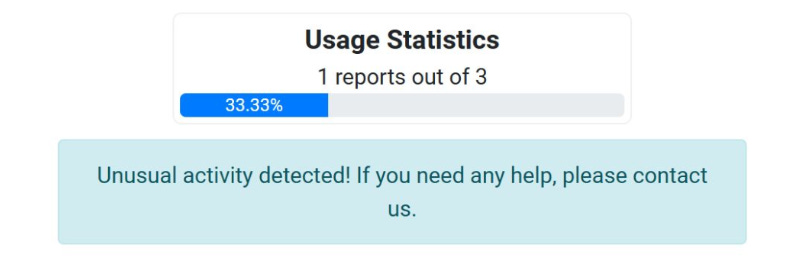
Based on my tests, this script only works in headful mode (headless=False). If you run it in headless mode (headless=True), you should get the following error page:
Notice the “Unusual activity detected! If you need any help, please contact us.” message (which is the same one that appears when calling the API directly using previous CAPTCHA-solving services).
nodriver ✅
nodriver is an open-source Python library that claims to be the successor to undetected-chromedriver (which hasn’t received major updates in over two years).
In particular, nodriver provides a blazing-fast framework for web automation, web scraping, and bot development, with built-in features to bypass anti-bot systems. These capabilities should be enough to overcome reCAPTCHA v3, as demonstrated by the following script:
# pip install nodriver
import nodriver
import asyncio
async def main():
# Start the browser
browser = await nodriver.start(headless=False)
# Navigate to the target page
page = await browser.get("https://completedns.com/dns-history")
# Wait for the page to load
await asyncio.sleep(10)
# Type the domain
input_box = await page.select("#domain")
await input_box.send_keys("google.com")
# Click the submit button
submit_button = await page.select("button[type='submit']")
await submit_button.click()
# Wait for the result to appear
await asyncio.sleep(10)
# Screenshot the whole page
await page.save_screenshot(filename="screenshot.png", full_page=True)
# Close the browser
await page.close()
if __name__ == "__main__":
nodriver.loop().run_until_complete(main())Just like with SeleniumBase, the reCAPTCHA v3 bypass script will only work in headful mode (headless=False). The produced screenshot.png file should contain:
Also, I occasionally got detected. That’s likely due to the level of randomization the library applies to spoof realistic browser fingerprints.
OpenAI Operator (now included in OpenAI Agent) ✅
OpenAI's Operator is an AI agent developed to autonomously perform tasks on the web. It’s a premium solution available exclusively to ChatGPT Pro users (which costs $200/month, so definitely not for every budget).
You can test whether it works against the target site using a simple prompt like:
Go to https://completedns.com/dns-history/ and submit the domain google.com, to extract the history of its DNSThe result should be similar to this recording.
Operator's AI agent bypasses reCAPTCHA v3 with no effort. That said, I have to admit that when I first tested it after launch, it struggled with other types of CAPTCHAs (sometimes producing hilariously bad results).
The technology has either improved in the meantime (which is likely), or it was just a lucky run (less likely).
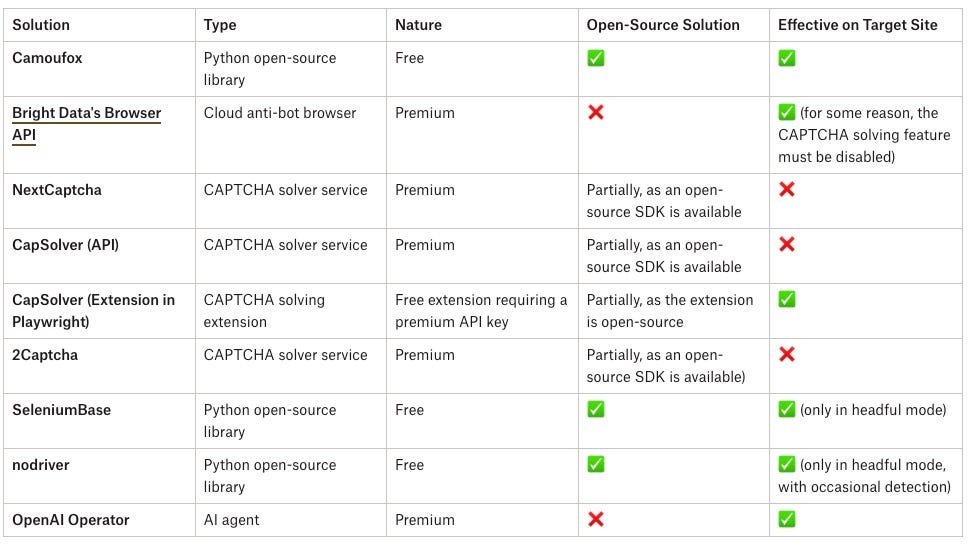
Conclusion
Compare the reCAPTCHA bypass solutions tested by me and Pierluigi (in part 1) in the summary table below:
If you’d like to see other tools tested or have solutions or approaches to recommend, feel free to let me know in the comments below!